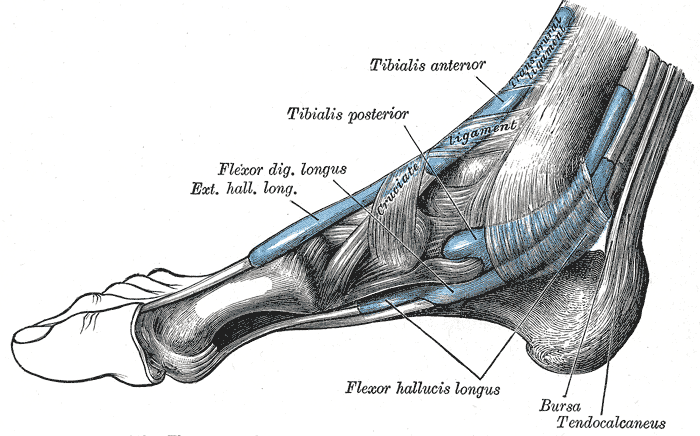
Tarsal tunnel syndrome (TTS) occurs when the tibial nerve is compressed within the tarsal tunnel (the area along the inner leg behind inside of the ankle) by inflamed tissue, a swollen blood vessel, or a tumor.
Anything that occupies space and creates pressure in the Tarsal Tunnel can cause TTS. This includes cysts, bone spurs, nerve ganglions, inflammation of the tendon sheath, or swelling from an injured ankle. Flat feet are also a risk factor as they cause pressure in the tunnel region and this can lead to nerve compression.
Symptoms of tarsal tunnel syndrome may include:
- Shooting pain in the foot.
- Numbness and tingling.
- Burning or electrical sensations.
Nonsurgical treatments for tarsal tunnel syndrome may include anti-inflammatory medications, steroid injections, foot orthotics, and physical therapy. When nonsurgical treatments fail, tarsal tunnel release surgery may be recommended to remove space-occupying masses.