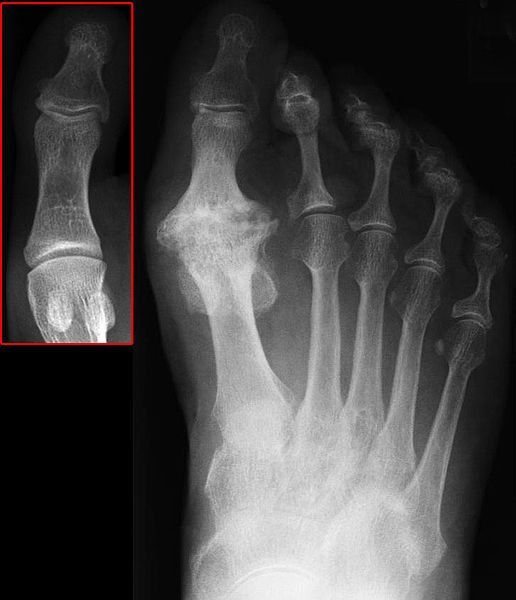
Degenerative joint disease (DJD) of the great toe joint, also called hallux rigidus (literally meaning “stiff great toe”) is when the joint at the great toe becomes, enlarged, misshapen, painful, and stiff. This condition includes mild to severe degenerative arthritis of the great toe joint and symptoms can range from mild to disabling. It is the most common arthritic condition of the foot and typically develops in adults between the ages of 30 and 60 years old.
The true cause of DJD of the great toe is unknown. Most commonly, it is thought to be caused by wear and tear of the great toe joint. Risk factors include differences in foot anatomy, prior traumatic injury to the big toe, athletic activities involving running, and family history.
The most common symptom is pain on the top of the great toe while active, particularly when pushing off to walk. Swelling and stiffness may also be present around the great toe.
Early treatment of DJD of the great toe may include:
- Changes in footwear.
- Shoe inserts.
- Ice or heat packs.
- Anti-inflmmatory medications.